FPGA供电电源设计相关的技术文章
收藏
分享
脑图
FPGA供电电源设计相关的技术文章

要求
多路电压@不同的电流和纹波要求
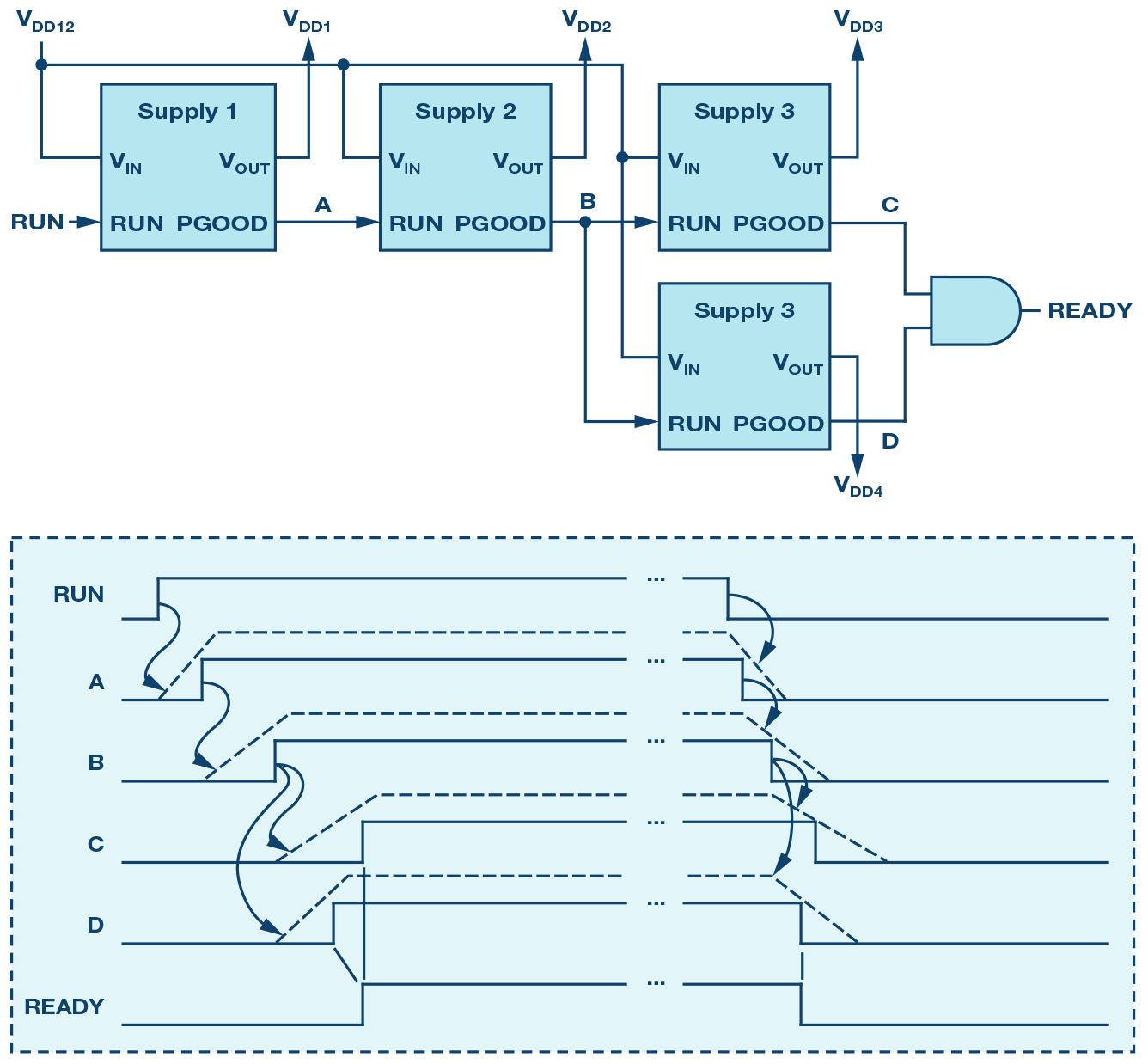
上电的时序要求
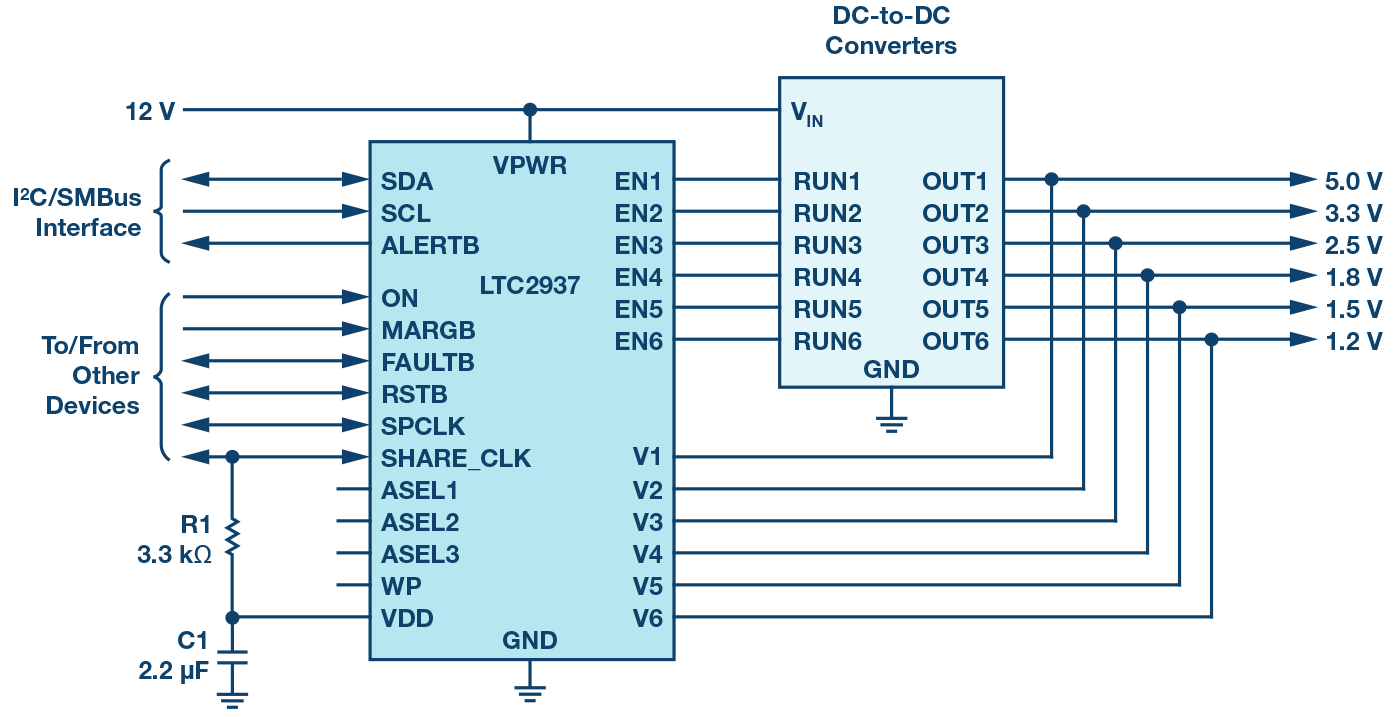
方案
TI的方案
ADI的方案
美信的方案
KINTEX ULTRASCALE PMBUS电源方案

KINTEX ULTRASCALE 、不带PMBUS总线的电源方案

瑞萨的方案
Altera/Intel的方案
文章
TI的文章
ADI的文章
相关器件
相关器件
美信的文章
瑞萨的文章
来自Intersil的产品说明
来自Intel的应用笔记
来自Power Electronic News的技术文章
来自Vishay的应用笔记
来自Semtech的应用笔记
来自Xilinx的视频教程
来自嵌入式计算机设计的技术文章
来自Power Electronics网站的技术文章
来自Electronic Design网站
来自Rohm官网
来自EETimes
来自Youtube的视频,由Altera/Intel提供
来自英飞凌官网
来自Electronical Engineering的讨论
来自Design&Reuse
来自Hackster网站上美信提供的Webinar
来自Altera/Intel的方案摘要
评论
0 / 100
查看更多
2019-11-22
3894
Copyright © 2024 苏州硬禾信息科技有限公司 All Rights Reserved 苏ICP备19040198号